Tuesday, May 10, 2016
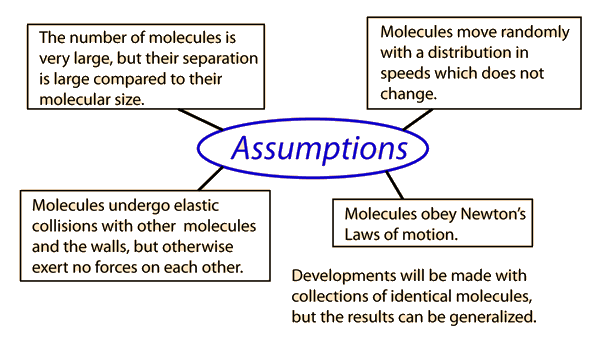
Kinetic Theory
Kinetic theory of gases is the bases for all seven of the gas laws. In this theory, subatomic particles in a gas, either atoms or molecules, are in an excited state of motion and the particles themselves have a randomness to them. They bounce against the wall of the container they are in and against each other. This theory is used for macroscopic properties of gas (gas as a whole, not individual particles), such as temperature, pressure, and volume.


Dalton's Gas Law
Another law. Only one more to go. This law is rather simple, but I'm kinda confused where you would use it. It talks about partial pressure, which is the pressure of one kind of gas in a container where multiple compounds are present. For example, if oxygen and water vapor are in the same container.


More Information
Ideal Gas Law
We learned about, yet, more laws. The next Law we learned about is The Ideal Gas Law.
This law can be when converting one has to another. R, the universal gas constant, is equal to .0821 L atm/ mol.
More Information
Hyperphysics
Kahnacadamy
Wednesday, May 4, 2016
Laws Laws Laws
This unit is focused properties of gases. So far we have gone over four of the seven gas laws. They are Boyle's, Charles', Avogadro's, and Combined Gas Law. They are all based off the master formula. These are all ideal gas laws
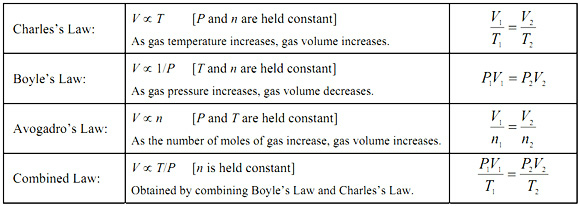
All of the laws keep at least on variable constant, and are either directly for indirectly proportional.
Extra Info:
Gas Laws
Chem Purdue

All of the laws keep at least on variable constant, and are either directly for indirectly proportional.
Extra Info:
Gas Laws
Chem Purdue
Tuesday, May 3, 2016
Phase Diagrams
A phase diagrams is a representation of the states of a substance in relation to temperature and pressure. This basically means that a phase diagram tells tells what physical phase (solid, liquid, gas), depending on the pressure and temperature.

We also leaned about heat/cooling curves, which compares heat added and temperature
. 

Extra Information:
Monday, May 2, 2016
m=CΔt
After we were done with all of the biodiesle projects, we started on a unit focused on energy. During this unit we will be looking at numerous systems and determining how the energy flows in and out of the system.
There are two different types of systems, endothermic and exothermic. Endothermic reactions gain energy from the surroundings, with a net energy gain. Exothermic reactions loose energy to their surrounding , with a net energy loss.


Next we leaned about how to calculate heat using a formula that looks like M-Cat. m=CΔt allows you calculate change of heat, mass of sample, amount of heat, or temperature
.
c is specific for a certain material, for example c for water is 4.186, while the specific heat capacity for copper is .385.
More info
BBC
Chem Wiki
Hyper-physics
There are two different types of systems, endothermic and exothermic. Endothermic reactions gain energy from the surroundings, with a net energy gain. Exothermic reactions loose energy to their surrounding , with a net energy loss.

Next we leaned about how to calculate heat using a formula that looks like M-Cat. m=CΔt allows you calculate change of heat, mass of sample, amount of heat, or temperature
.
c is specific for a certain material, for example c for water is 4.186, while the specific heat capacity for copper is .385.
More info
BBC
Chem Wiki
Hyper-physics
Tuesday, April 19, 2016
Put-Put Boat
Using the biodiesel from the lab we made Put-Put boats using it to race. Put-Put boats use steam engine to propel themselves forward, and can be made out of anything that floats. Not all we made were good, my group in particular.


Links
Links
http://www.sciencetoymaker.org/boat/asembCartonl.html
Monday, April 18, 2016
Making Biodiesel
For the next part of the biodiesel unit, we made biodiesel from some pretty gross looking stuff. Taking used geese from chik-fillet a and some other compounds, then mixing them in heat, we were able to create burnable biodiesel. It wasn't particularity hard and can be done at home. (Warning: unpleasant smell)


Link:
http://www.make-biodiesel.org/
http://journeytoforever.org/biodiesel_make.html

Link:
http://www.make-biodiesel.org/
http://journeytoforever.org/biodiesel_make.html
Sunday, April 17, 2016
Biodiesel
Our next project in class is to put together a video to enter in a competition. The video must be supportive of biodiesel and the winner is the video with the most views. My lab partner decided to make a video of Uncle Sam encouraging the viewer to use biodiesel for the good of the U.S. We had to find a lot of facts on biodiesel, and we found this:


Links:
http://biodiesel.org/
https://www.fueleconomy.gov/feg/biodiesel.shtml


Links:
http://biodiesel.org/
https://www.fueleconomy.gov/feg/biodiesel.shtml
Wednesday, March 16, 2016
Hybridization and Resonance
Hybridization looks similar to locations of electrons, but the amount of space in each sub-level is counting the number of orbitals, not the number of electrons. More information can be found here.
The resonance of a molecule or ion were the bond aren't all the same (all either single, double, or triple) and the other bonded atoms can take the bond that is being moved, were the double or triples bonds are can switch. Basically the Lewis dot structure of a molecule or ion can be drawn in multiple ways.
| Carbon trioxide had resonance |
The structure with the mean resonance is called the resonance hybrid. This is the most accurate form of the molecule or ion. It equalizes bond length and strength. More infomation if resonance can be found here.
Monday, March 14, 2016
VSEPR
Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Theory (VSEPR) is used to predict the molecular shape of a molecule. Unlike a Lewis Dot Structure, VSEPR is in three dimensions, and thus, is more accurate; however, takes longer to find.
| Nitrogen trioxide |
The wedges and lines show that the bonds move towards or away form you, thus giving the bond it's 3-D shape. The shape of a molecule determines how it acts towards other molecules. The example given above is polar, so the molecule has a charge and reacts differently than a molecule that is non-polar would. Each shape also had a unique electron geometry, which depends on its number of electron domains around its central atom. The example is tetrahedral, because their is four electron domains around the nitrogen, three bonds and one pair.
Sunday, March 13, 2016
Lewis Dot Stucture
No more ionic bonds, and its terrible. This unit is over how covalent bonds bonds look. This can be done on a two dimensional plane, called a Lewis Dot Structure. The structure tells you what atoms have electrons and which atoms share electrons with other atoms.
The dots next to each elements tell the number of electrons that stay next to each element. The lines represent two electrons that are shared between elements. The total number of electrons in the structure have to equal the total number of valence electrons of the elements. The number of bonds needed can be found using a have, need, share method.
Saturday, March 5, 2016
Post-Test Thoughts
Long. 50 questions in less than one hour is hard to finish, thankfully where wasn't a lot of math after the first 10 or so questions. Overall I fell pretty good about that test, was able to finish in time and not guess on a whole bunch of the question. Should probally start studying more by doing the practice quizzes. Still, overall, felt pretty good about it.
Quantum Numbers
Quantum numbers seem like a more confusing way of organizing atoms on the periodic table. Basically they look like this:

I am not totally sure what quantum numbers are used for, so the other type of organization works just fine. I would guess that they would be used for higher levels of mathematics and physics that deal with quantum mechanics.
Thursday, March 3, 2016
Pre-Test Worries
After doing rather well on this quiz I hope that I do well with this test. The last few tests have been rather hard, but I do think that I have a good chance to do well on this one, if I study.
Organization
Besides just using the names of the atoms, it is possible to categorize atoms form one another by using a method of organization. There are four levels, going from principle energy level, sublevel, orbital, and spin. Principle energy level is normal equal to the period which an element resided, exept if the atom is a rare earth metal or a transition metal. Sublevel depends on what block the atom resides in -- metal, transition metal, non-metal, and rare earth metal. Orbitals depend of sublevel, and spin depends on number of electrons.
Here is a detailed way of how the atoms are named in this method.
Monday, February 22, 2016
Electronic Structure
Waves, we leaned about waves. And no, not the really cool ocean waves, but the waves of subatomic particles (electrons). So apparently electrons like to move in a wave like nature, where they oscillate back and forth. I don't think anyone knows why they do this, but rather accept it was reality. There is also many things that are to be known about these waves:
Using math, it becomes possible to find the values of some of these variables (wavelengh and amplitude) by using he equation:
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)
