Tuesday, May 10, 2016
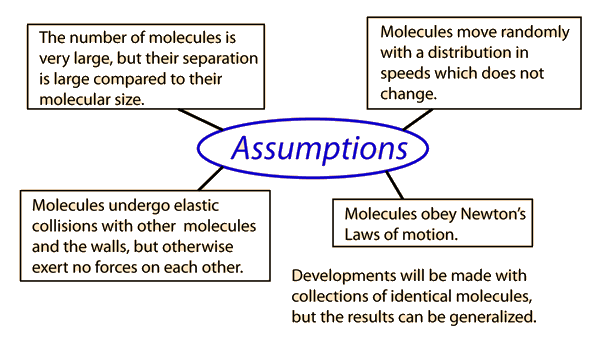
Kinetic Theory
Kinetic theory of gases is the bases for all seven of the gas laws. In this theory, subatomic particles in a gas, either atoms or molecules, are in an excited state of motion and the particles themselves have a randomness to them. They bounce against the wall of the container they are in and against each other. This theory is used for macroscopic properties of gas (gas as a whole, not individual particles), such as temperature, pressure, and volume.


Dalton's Gas Law
Another law. Only one more to go. This law is rather simple, but I'm kinda confused where you would use it. It talks about partial pressure, which is the pressure of one kind of gas in a container where multiple compounds are present. For example, if oxygen and water vapor are in the same container.


More Information
Ideal Gas Law
We learned about, yet, more laws. The next Law we learned about is The Ideal Gas Law.
This law can be when converting one has to another. R, the universal gas constant, is equal to .0821 L atm/ mol.
More Information
Hyperphysics
Kahnacadamy
Wednesday, May 4, 2016
Laws Laws Laws
This unit is focused properties of gases. So far we have gone over four of the seven gas laws. They are Boyle's, Charles', Avogadro's, and Combined Gas Law. They are all based off the master formula. These are all ideal gas laws
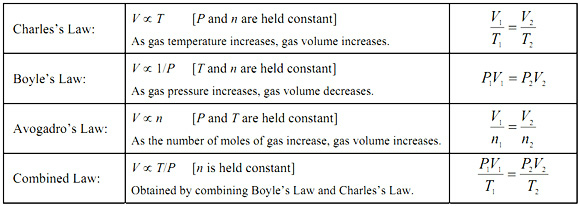
All of the laws keep at least on variable constant, and are either directly for indirectly proportional.
Extra Info:
Gas Laws
Chem Purdue

All of the laws keep at least on variable constant, and are either directly for indirectly proportional.
Extra Info:
Gas Laws
Chem Purdue
Tuesday, May 3, 2016
Phase Diagrams
A phase diagrams is a representation of the states of a substance in relation to temperature and pressure. This basically means that a phase diagram tells tells what physical phase (solid, liquid, gas), depending on the pressure and temperature.

We also leaned about heat/cooling curves, which compares heat added and temperature
. 

Extra Information:
Monday, May 2, 2016
m=CΔt
After we were done with all of the biodiesle projects, we started on a unit focused on energy. During this unit we will be looking at numerous systems and determining how the energy flows in and out of the system.
There are two different types of systems, endothermic and exothermic. Endothermic reactions gain energy from the surroundings, with a net energy gain. Exothermic reactions loose energy to their surrounding , with a net energy loss.


Next we leaned about how to calculate heat using a formula that looks like M-Cat. m=CΔt allows you calculate change of heat, mass of sample, amount of heat, or temperature
.
c is specific for a certain material, for example c for water is 4.186, while the specific heat capacity for copper is .385.
More info
BBC
Chem Wiki
Hyper-physics
There are two different types of systems, endothermic and exothermic. Endothermic reactions gain energy from the surroundings, with a net energy gain. Exothermic reactions loose energy to their surrounding , with a net energy loss.

Next we leaned about how to calculate heat using a formula that looks like M-Cat. m=CΔt allows you calculate change of heat, mass of sample, amount of heat, or temperature
.
c is specific for a certain material, for example c for water is 4.186, while the specific heat capacity for copper is .385.
More info
BBC
Chem Wiki
Hyper-physics
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)
